27.11.2015
At the same time, cases of failure or complete absence of electric power is not infrequent. In this case, there is a need to provide the power supply to especially vital systems, such as heating, communication, security and fire alarm systems. To avoid failures in their operation, it is worthwhile to install a device or uninterruptible power supply system.
An Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) is a source of secondary power supply, automatic device designed to provide the uninterruptible electric energy supply within the normal range to the electrical equipment connected to it. UPS enables to continue operation of the equipment connected to it during the period of a power supply failure. And a built-in automatic voltage regulator provides qualitative power supply after decline or increase of the mains voltage, as well as it protects equipment against interferences and voltage jumps in the mains.
Such UPS controls the mains indexes constantly; it corrects the mains voltage automatically or switches over to the battery operation mode ensuring continuous operation of the equipment.
In order to protect the equipment properly, it is necessary to select correctly an uninterruptible power supply system, which will correspond to the protected equipment.
There are three main types of the most widespread uninterruptible power supplies:
1. Uninterruptible power supplies of Off-Line type
In the normal operation mode of Off-Line UPS, the power is supplied to the load with the filtered voltage of the primary mains. If input voltage parameters go beyond the values of a preset range, the device is switched over to the battery operation mode, irrespective of whether there is voltage in the mains or not. This imposes certain limits on such devices:
• they are applicable only in mains with stable quality of electric energy;
• they have bad protection against voltage depressions exceeding admissible values, frequency changes and input voltage forms;
• impossibility to renew capacity of storage batteries timely due to frequent switching over to the battery operation;
• due to the great voltage spread in the mains, especially outside big cities, Off-Line UPS can be used adequately only jointly with an additional automatic voltage regulator.
2. Uninterruptible power supplies of On-Line type
In the normal operation mode of On-Line UPS, the mains voltage is rectified and then it is converted into direct voltage for a battery charging and power supply to the output stage.
When the mains voltage is sufficient, the output stage transforms direct voltage into sinusoidal voltage 220 V. When the mains voltage is lower, the current shortage is compensated by a battery; when the voltage is absent in the mains, the power is supplied from the battery only.
Power supply quality and operation reliability of such a device are significantly higher in comparison with the previous type. However, this device has shortcomings after all:
• low coefficient of efficiency as compared with other UPS types because of double conversion;
• high cost;
• relatively small battery resource.
Such UPS are mostly used to maintain the operation of servers and routers in the corporate mains.
3. Uninterruptible power supplies of Line-Interactive type
Line-interactive UPS combine advantages of uninterruptible power supplies discussed above; their shortcomings were minimized wherever it was possible.
The built-in automatic voltage regulator provides qualitative power supply when the mains voltage is high or low, as well as it protects equipment against interferences and mains voltage jumps.
When the input voltage parameters are beyond the operating range, the power is supplied from a battery, which provides the power supply continuity.
Along with the number of advantages, these devices have some disadvantages. The nonzero switching over time (4-10 ms) to batteries is a shortcoming of line-interactive UPS, but in most cases, it is not critical for consumers.
In its turn UPS of such type are subdivided into:
• UPS with the output approximated sinusoid (it suits only for devices with pulse power units);
• more unified UPS with the regular shape sinusoid, which apart from the above-mentioned can operate with devices critical to the input current form (with transformers, motors, compressors, etc.).
UPS of Line-Interactive type is the most optimal choice for the uninterruptible power supply system, based on the price, consumer properties, coefficient of efficiency and battery resource.
The power supply problem becomes especially acute in winter due to the load increase to the mains. Weather deterioration frequently results in breakdowns of power transmission lines.
The autonomous heating system becomes one of the most vulnerable systems in these conditions. Of course, the operation stoppage of a heating system during the winter season for a long time can cause the considerable damage. Because voltage swings and power failures lead to the heating boiler stoppage, on frequent occasions they provoke its malfunctions.
In the first place, the force circulation of a heat-transfer agent in modern heating systems is supported with the help of electric circulation pumps. In the second place, some modifications of boilers have air boost systems into a combustion chamber and removal of products of combustion based on electric fans, as well as microprocessor control units.
Such heating system operates as follows:
A thermostat controls the air temperature in an apartment. When temperature changes, the thermal load is also changed, and consequently the required fuel amount. Energy due to gas combustion heats the heat-transfer agent in the heat exchanger. A manometer and thermometer control the heat-transfer agent indices. The circulation pump runs the heat-transfer agent along the heating loop. The whole device operation is controlled by the electronic control unit.
A correctly selected uninterruptible power supply with a battery will enable to avoid problems related to the boiler stop or its out of order due to voltage swings in the mains, as well as to provide its operation within the time required.
Fitting criteria of UPS for a modern boiler
When selecting an uninterruptible power supply for the boiler it is necessary to take into account that the output voltage form of UPS must be sinusoidal, because the boiler contains devices-consumers critical to the input current form (fan, circulating pump, etc.).
In order not to avoid mistakes when selecting an UPS, it is necessary to find answers to the following questions:
• Power consumption in modern boilers is small. It ranges as a rule within limits from 80 to 300 W;
• Autonomous operation time, during which UPS must provide the load. In order the boiler operates for several hours in the absence of power supply in the mains, it is necessary to buy UPS with a possibility to connect external blocks of batteries. Depending on a required self-contained operation time, the necessary capacity of battery is selected. Pay also attention to the protection of batteries against over discharging. When batteries are over discharged (below permissible level), their capacity decreases quickly, that leads to the self-contained operation time reduction;
• Built-in automatic voltage regulator. Pay attention to the quality of the mains. If there are great voltage fluctuations in the mains, then the input voltage range of AVR is an important characteristic for the UPS choice: the wider the range, the rarer UPS will be switched over to the battery operation and this will increase the battery lifetime. It is better to select UPS with a built-in AVR.
UPS of HOME series developed and produced by the Company is an ideal solution for the uninterruptible power supply of heating systems, intellectual fire-fighting and alarm systems, automation systems, etc.
Continuous backup power supply is realized due to considerable, changeable in wide limits capacity of external batteries.
The built-in automatic voltage regulator makes it possible to provide the correct power supply, when the mains voltage is low or high without switching to the battery operation mode. This enables to save the battery (batteries) resource considerably.
In order to select a Home UPS model, it is necessary to calculate the total power (W) of equipment connected to UPS (it is given in technical documentation of equipment).
Select UPS Home model (500 or 1000) depending on the power from the table:
Select the battery(ies) capacity depending on the power of connected load and the required power reserve time, see tables 1 and 2 below:
Structural diagram of uninterruptible power supply network
The set assembly and connection presents no problems.
The uninterruptible power supply set has been developed in such a way that its assembly and connection does not cause difficulties for users, who do not have special qualification.
1. Place the set (Home UPS + batteries) in a site chosen by you with good ventilation (free space around UPS must be not less than 25 cm).
2. Connect a battery (purchased separately) to UPS power terminals observing a polarity using supplied cables. Pay attention, in case of using several batteries, connect the batteries IN PARALLEL, observing a polarity. Let us remind that a positive terminal is always red, but a negative terminal is black or blue. While connecting two or more batteries, a positive terminal of one battery is connected to a positive terminal of the other, negative terminals of batteries are connected in a like manner. Additional cables (purchased separately) will be required to connect additional batteries.
3. Connect UPS Home to a socket of the single-phase mains (desirably with grounding) using the built-in power cord. After connection the battery will be charged, digital LCD display is turned on (see Fig. below) and there will be four short beeps. The output voltage indicator 1 will display the inscription “220”. At that the battery charge level is controlled by five-segment indicator 3 (every segment is equal approximately 20 % capacity).
There is no need to turn on Home UPS after its connection to the mains – the autostart function will start it automatically.
4. Leave the device in the “on” condition until the completion battery charging (6-12 hours). Battery charge level indicator 6 (all five segments of the indicator must be illuminated) will signal about the charge completion).
5. Press and hold button “Mains” – a single beep must sound – the device is disconnected, at that, the output voltage indicator must display figures “000”.
6. Then disconnect the power cord plug from the mains and connect devices-consumers to the disconnected device.
7. After connection of devices-consumers, insert the plug of Home UPS into a socket and then turn on the connected devices with their switches (if they are available).
UPS is ready for operation!
UPS control panel with display
Important elaborations:
In case of Home UPS forced shutdown, first of all turn off the devices connected to it using their switches, then act according to the UPS disconnection instruction. Press and hold the “Mains” button – a beep signal must sound – the device will be disconnected; at that, the numerals “000” must be displayed on the output voltage indicator.
For restarting press and hold the “Mains” button of Home UPS, while a beep signal sounds and the inscription “220” is on the output voltage indicator (7).
At the moment of switching over to the battery operation (after the power failure) Home UPS provides the beep signal as well. During the battery operation, the beep signals are repeated every 30 seconds.
If the battery charge level is low (during battery operation mode), UPS begins to provide beep signals every second. When the battery voltage is less than 10.5 V, UPS is turned off automatically.
If the load is too great, UPS starts to provide beep signals within 60 seconds and then it is turned off.
Beep signal cutoff is envisaged in Home UPS. For this purpose press and hold the “Sound” button (a distinctive long beep signal), while beep signals are over. If it is necessary to restart beep signals, repeat the procedure described above.
When two or more batteries are used (connected in parallel), you should remember that they must be of one type and capacity (if rate values of battery capacities differ, consequently, they have different internal resistance, as well as the charge level, in consequence of which their service life is decreased).
Home UPS can be tuned on using the “Cold start” function (without connecting to the mains). Press and hold the “Mains” button on UPS, the beep signal is sound, UPS will be turned on and the power will be supplied to devices-consumers. It is not recommended to use this function the battery charge is low.
Do not use motorcar batteries: they badly bear the discharge lower than 12 V (UPS disconnects the batteries with the residual voltage 10.5 V) and they quickly get out of order.
If there is no need to use systems for a long time, UPS should be disconnected from the mains and batteries are to be disconnected from the UPS. It is recommended to recharge batteries every six months.
Home UPS Series
It is no secret that the AC mains in use are far from the ideal. Most often, a reason of failures of electronic devices is the off-grade power supply. Partially this problem can be solved at the cost of using devices for the improvement of power supply quality, such, for example, as automatic voltage regulators.
At the same time, cases of failure or complete absence of electric power is not infrequent. In this case, there is a need to provide the power supply to especially vital systems, such as heating, communication, security and fire alarm systems. To avoid failures in their operation, it is worthwhile to install a device or uninterruptible power supply system.
An Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) is a source of secondary power supply, automatic device designed to provide the uninterruptible electric energy supply within the normal range to the electrical equipment connected to it. UPS enables to continue operation of the equipment connected to it during the period of a power supply failure. And a built-in automatic voltage regulator provides qualitative power supply after decline or increase of the mains voltage, as well as it protects equipment against interferences and voltage jumps in the mains.
Such UPS controls the mains indexes constantly; it corrects the mains voltage automatically or switches over to the battery operation mode ensuring continuous operation of the equipment.
In order to protect the equipment properly, it is necessary to select correctly an uninterruptible power supply system, which will correspond to the protected equipment.
There are three main types of the most widespread uninterruptible power supplies:
1. Uninterruptible power supplies of Off-Line type
In the normal operation mode of Off-Line UPS, the power is supplied to the load with the filtered voltage of the primary mains. If input voltage parameters go beyond the values of a preset range, the device is switched over to the battery operation mode, irrespective of whether there is voltage in the mains or not. This imposes certain limits on such devices:
• they are applicable only in mains with stable quality of electric energy;
• they have bad protection against voltage depressions exceeding admissible values, frequency changes and input voltage forms;
• impossibility to renew capacity of storage batteries timely due to frequent switching over to the battery operation;
• due to the great voltage spread in the mains, especially outside big cities, Off-Line UPS can be used adequately only jointly with an additional automatic voltage regulator.
2. Uninterruptible power supplies of On-Line type
In the normal operation mode of On-Line UPS, the mains voltage is rectified and then it is converted into direct voltage for a battery charging and power supply to the output stage.
When the mains voltage is sufficient, the output stage transforms direct voltage into sinusoidal voltage 220 V. When the mains voltage is lower, the current shortage is compensated by a battery; when the voltage is absent in the mains, the power is supplied from the battery only.
Power supply quality and operation reliability of such a device are significantly higher in comparison with the previous type. However, this device has shortcomings after all:
• low coefficient of efficiency as compared with other UPS types because of double conversion;
• high cost;
• relatively small battery resource.
Such UPS are mostly used to maintain the operation of servers and routers in the corporate mains.
3. Uninterruptible power supplies of Line-Interactive type
Line-interactive UPS combine advantages of uninterruptible power supplies discussed above; their shortcomings were minimized wherever it was possible.
The built-in automatic voltage regulator provides qualitative power supply when the mains voltage is high or low, as well as it protects equipment against interferences and mains voltage jumps.
When the input voltage parameters are beyond the operating range, the power is supplied from a battery, which provides the power supply continuity.
Along with the number of advantages, these devices have some disadvantages. The nonzero switching over time (4-10 ms) to batteries is a shortcoming of line-interactive UPS, but in most cases, it is not critical for consumers.
In its turn UPS of such type are subdivided into:
• UPS with the output approximated sinusoid (it suits only for devices with pulse power units);
• more unified UPS with the regular shape sinusoid, which apart from the above-mentioned can operate with devices critical to the input current form (with transformers, motors, compressors, etc.).
UPS of Line-Interactive type is the most optimal choice for the uninterruptible power supply system, based on the price, consumer properties, coefficient of efficiency and battery resource.
The power supply problem becomes especially acute in winter due to the load increase to the mains. Weather deterioration frequently results in breakdowns of power transmission lines.
The autonomous heating system becomes one of the most vulnerable systems in these conditions. Of course, the operation stoppage of a heating system during the winter season for a long time can cause the considerable damage. Because voltage swings and power failures lead to the heating boiler stoppage, on frequent occasions they provoke its malfunctions.
In the first place, the force circulation of a heat-transfer agent in modern heating systems is supported with the help of electric circulation pumps. In the second place, some modifications of boilers have air boost systems into a combustion chamber and removal of products of combustion based on electric fans, as well as microprocessor control units.
Such heating system operates as follows:
A thermostat controls the air temperature in an apartment. When temperature changes, the thermal load is also changed, and consequently the required fuel amount. Energy due to gas combustion heats the heat-transfer agent in the heat exchanger. A manometer and thermometer control the heat-transfer agent indices. The circulation pump runs the heat-transfer agent along the heating loop. The whole device operation is controlled by the electronic control unit.
A correctly selected uninterruptible power supply with a battery will enable to avoid problems related to the boiler stop or its out of order due to voltage swings in the mains, as well as to provide its operation within the time required.
Fitting criteria of UPS for a modern boiler
When selecting an uninterruptible power supply for the boiler it is necessary to take into account that the output voltage form of UPS must be sinusoidal, because the boiler contains devices-consumers critical to the input current form (fan, circulating pump, etc.).
In order not to avoid mistakes when selecting an UPS, it is necessary to find answers to the following questions:
• Power consumption in modern boilers is small. It ranges as a rule within limits from 80 to 300 W;
• Autonomous operation time, during which UPS must provide the load. In order the boiler operates for several hours in the absence of power supply in the mains, it is necessary to buy UPS with a possibility to connect external blocks of batteries. Depending on a required self-contained operation time, the necessary capacity of battery is selected. Pay also attention to the protection of batteries against over discharging. When batteries are over discharged (below permissible level), their capacity decreases quickly, that leads to the self-contained operation time reduction;
• Built-in automatic voltage regulator. Pay attention to the quality of the mains. If there are great voltage fluctuations in the mains, then the input voltage range of AVR is an important characteristic for the UPS choice: the wider the range, the rarer UPS will be switched over to the battery operation and this will increase the battery lifetime. It is better to select UPS with a built-in AVR.
UPS of HOME series developed and produced by the Company is an ideal solution for the uninterruptible power supply of heating systems, intellectual fire-fighting and alarm systems, automation systems, etc.
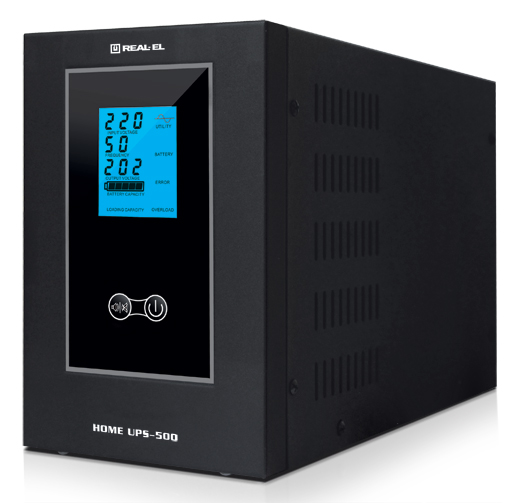

Home UPS-500 uninterruptible power supply |
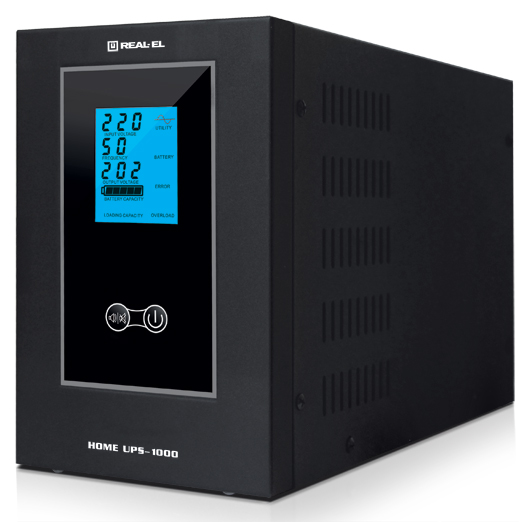

Home UPS-1000 uninterruptible power supply |
A correct outlet sine signal enables to provide the uninterruptible power supply of consumers, which are critical to the current supply form.
Continuous backup power supply is realized due to considerable, changeable in wide limits capacity of external batteries.
The built-in automatic voltage regulator makes it possible to provide the correct power supply, when the mains voltage is low or high without switching to the battery operation mode. This enables to save the battery (batteries) resource considerably.
In order to select a Home UPS model, it is necessary to calculate the total power (W) of equipment connected to UPS (it is given in technical documentation of equipment).
Select UPS Home model (500 or 1000) depending on the power from the table:
 |
Select the battery(ies) capacity depending on the power of connected load and the required power reserve time, see tables 1 and 2 below:
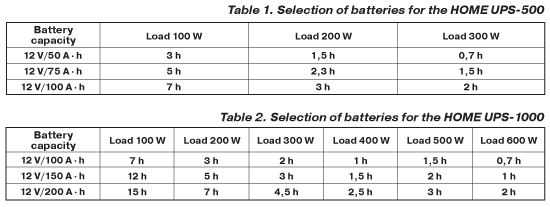 |
Structural diagram of uninterruptible power supply network
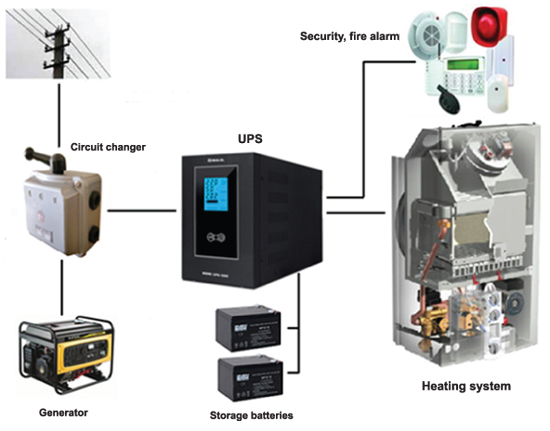
UPS connection diagram |
The set assembly and connection presents no problems.
The uninterruptible power supply set has been developed in such a way that its assembly and connection does not cause difficulties for users, who do not have special qualification.
1. Place the set (Home UPS + batteries) in a site chosen by you with good ventilation (free space around UPS must be not less than 25 cm).
2. Connect a battery (purchased separately) to UPS power terminals observing a polarity using supplied cables. Pay attention, in case of using several batteries, connect the batteries IN PARALLEL, observing a polarity. Let us remind that a positive terminal is always red, but a negative terminal is black or blue. While connecting two or more batteries, a positive terminal of one battery is connected to a positive terminal of the other, negative terminals of batteries are connected in a like manner. Additional cables (purchased separately) will be required to connect additional batteries.
3. Connect UPS Home to a socket of the single-phase mains (desirably with grounding) using the built-in power cord. After connection the battery will be charged, digital LCD display is turned on (see Fig. below) and there will be four short beeps. The output voltage indicator 1 will display the inscription “220”. At that the battery charge level is controlled by five-segment indicator 3 (every segment is equal approximately 20 % capacity).
There is no need to turn on Home UPS after its connection to the mains – the autostart function will start it automatically.
4. Leave the device in the “on” condition until the completion battery charging (6-12 hours). Battery charge level indicator 6 (all five segments of the indicator must be illuminated) will signal about the charge completion).
5. Press and hold button “Mains” – a single beep must sound – the device is disconnected, at that, the output voltage indicator must display figures “000”.
6. Then disconnect the power cord plug from the mains and connect devices-consumers to the disconnected device.
7. After connection of devices-consumers, insert the plug of Home UPS into a socket and then turn on the connected devices with their switches (if they are available).
UPS is ready for operation!
UPS control panel with display
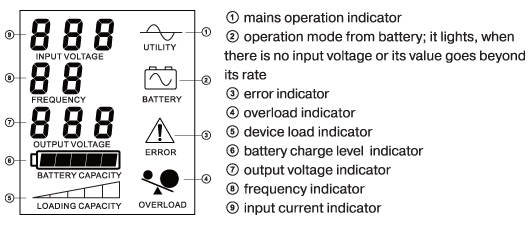
UPS display description |
Important elaborations:
In case of Home UPS forced shutdown, first of all turn off the devices connected to it using their switches, then act according to the UPS disconnection instruction. Press and hold the “Mains” button – a beep signal must sound – the device will be disconnected; at that, the numerals “000” must be displayed on the output voltage indicator.
For restarting press and hold the “Mains” button of Home UPS, while a beep signal sounds and the inscription “220” is on the output voltage indicator (7).
At the moment of switching over to the battery operation (after the power failure) Home UPS provides the beep signal as well. During the battery operation, the beep signals are repeated every 30 seconds.
If the battery charge level is low (during battery operation mode), UPS begins to provide beep signals every second. When the battery voltage is less than 10.5 V, UPS is turned off automatically.
If the load is too great, UPS starts to provide beep signals within 60 seconds and then it is turned off.
Beep signal cutoff is envisaged in Home UPS. For this purpose press and hold the “Sound” button (a distinctive long beep signal), while beep signals are over. If it is necessary to restart beep signals, repeat the procedure described above.
When two or more batteries are used (connected in parallel), you should remember that they must be of one type and capacity (if rate values of battery capacities differ, consequently, they have different internal resistance, as well as the charge level, in consequence of which their service life is decreased).
Home UPS can be tuned on using the “Cold start” function (without connecting to the mains). Press and hold the “Mains” button on UPS, the beep signal is sound, UPS will be turned on and the power will be supplied to devices-consumers. It is not recommended to use this function the battery charge is low.
Do not use motorcar batteries: they badly bear the discharge lower than 12 V (UPS disconnects the batteries with the residual voltage 10.5 V) and they quickly get out of order.
If there is no need to use systems for a long time, UPS should be disconnected from the mains and batteries are to be disconnected from the UPS. It is recommended to recharge batteries every six months.


